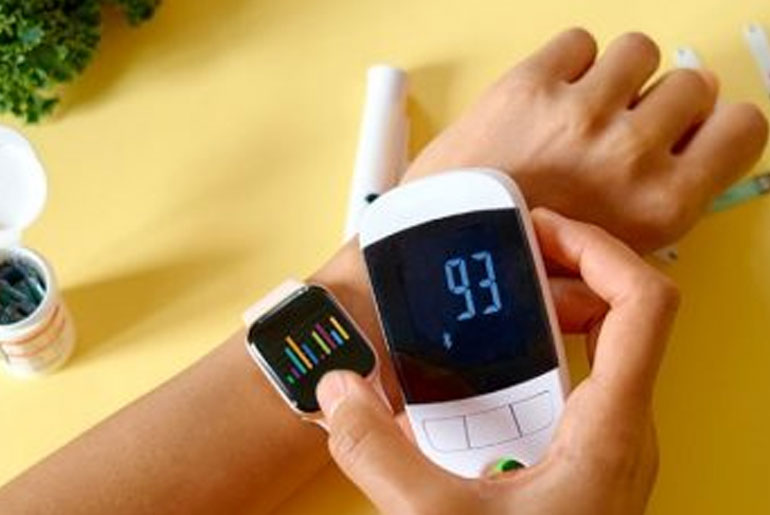
Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is essential for general health, particularly for people with diabetes or those who are treating the disease. Frequent exercise helps muscles absorb glucose from the bloodstream and improves the body’s usage of insulin. Fortunately, without the need for elaborate regimens or expensive equipment, basic and regular exercises can have a big impact. Here are a few efficient exercises with detailed explanations:
After each meal, taking a stroll
One of the easiest and most efficient strategies to control blood sugar is to take a walk after meals. After eating, blood glucose levels naturally rise; however, a quick walk of 10 to 15 minutes allows muscles to use this glucose for energy, minimizing spikes. Particularly after heavier meals like lunch and dinner, even a short walk around your house or neighborhood can help with digestion and enhance insulin sensitivity.
Strength Training
The secret to long-term blood sugar regulation is strength training. Squats, lunges, push-ups, and resistance band workouts are a few exercises that help increase muscle mass, which increases glycogen storage and lowers blood sugar levels. Additionally, this kind of exercise improves insulin function and increases metabolism. Two to three times a week, resistance training can greatly help maintain stable blood sugar control.
Calf Raises
An easy and efficient workout that you can perform practically anywhere is the calf lift. By using the big calf muscles, this exercise encourages circulation and effective glucose utilization. You may do this while cooking, waiting in line, or even while brushing your teeth. Just raise your heels off the ground and slowly lower them. For people who spend a lot of time sitting, performing 20–30 repetitions multiple times a day is extremely helpful.
Cardio Zone 2
Zone 2 cardio is moderate-intensity exercise that allows you to talk but not sing easily, such as brisk walking, light jogging, cycling, or swimming. Insulin sensitivity is increased, mitochondrial function is improved, and energy is largely obtained from fat and glucose. Three to five times a week, for 30 to 45 minutes, Zone 2 cardio promotes cardiovascular health and blood sugar control.
Quick Bursts of Vigorous Exercise
High-intensity interval training (HIIT), which consists of brief bursts of intense activity, can rapidly reduce blood sugar. This entails quick bursts of intense activity (like sprinting, jumping jacks, or fast squats) interspersed with shorter rest intervals. These exercises can enhance the muscles’ absorption of glucose for as little as five to ten minutes. Beginners should begin gradually and get medical advice if they have any underlying health issues.
In conclusion, complex routines are not necessary for blood sugar management. Simple routines like Zone 2 cardio, calf raises, strength training, walking after meals, and brief, high-intensity workouts can have a big impact. The secret is consistency. By incorporating these exercises into daily life, individuals can improve insulin sensitivity, prevent sudden glucose spikes, and support overall metabolic health in a safe and effective way.
Disclaimer:
The information contained in this article is for educational and informational purposes only and is not intended as a health advice. We would ask you to consult a qualified professional or medical expert to gain additional knowledge before you choose to consume any product or perform any exercise.